FLOW VPM
Meshless large eddy simulationthrough the reformulated vortex particle method
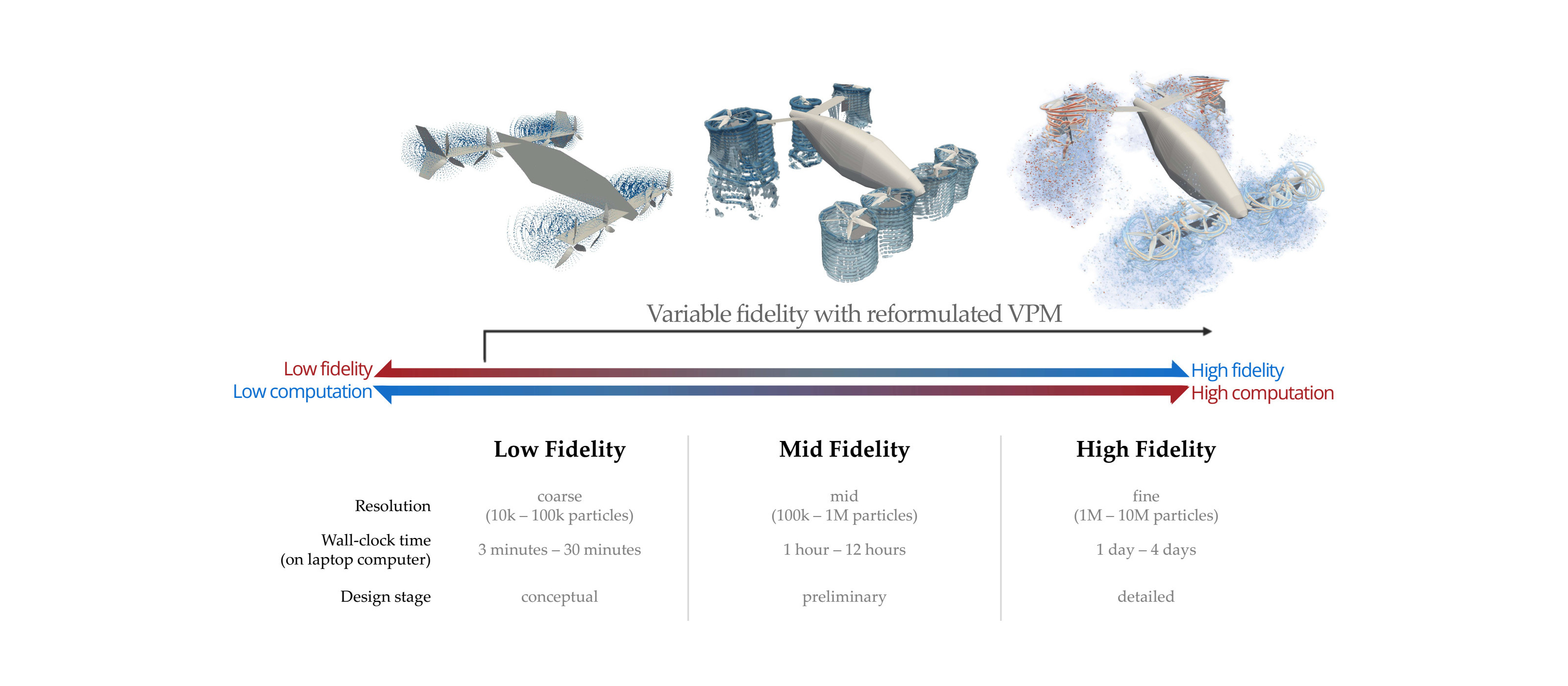
FLOWVPM implements the reformulated vortex particle method (rVPM) developed in my doctoral research. The rVPM is a CFD method solving the LES-filtered incompressible Navier-Stokes equations in their vorticity form. It uses a Lagrangian (meshless) scheme, which not only avoids the hurdles of mesh generation, but it also conserves vortical structures over long distances with minimal numerical dissipation.
The rVPM uses particles to discretize the Navier-Stokes equations, with the particles representing radial basis functions that construct a continuous vorticity/velocity field. The basis functions become the LES filter, providing a variable filter width and spatial adaption as the particles are convected and stretched by the velocity field. The local evolution of the filter width provides an extra degree of freedom to re-inforce conservations laws, which makes the reformulated VPM numerically stable.
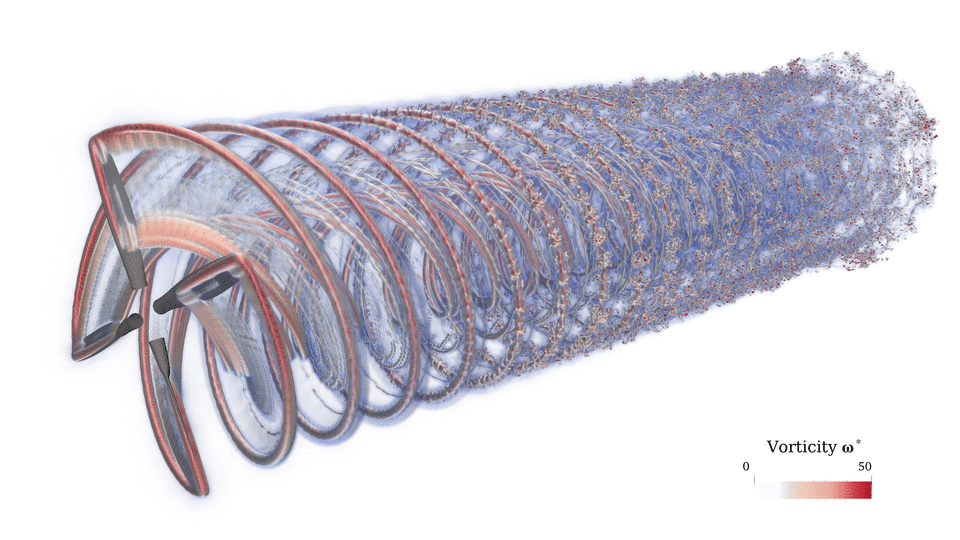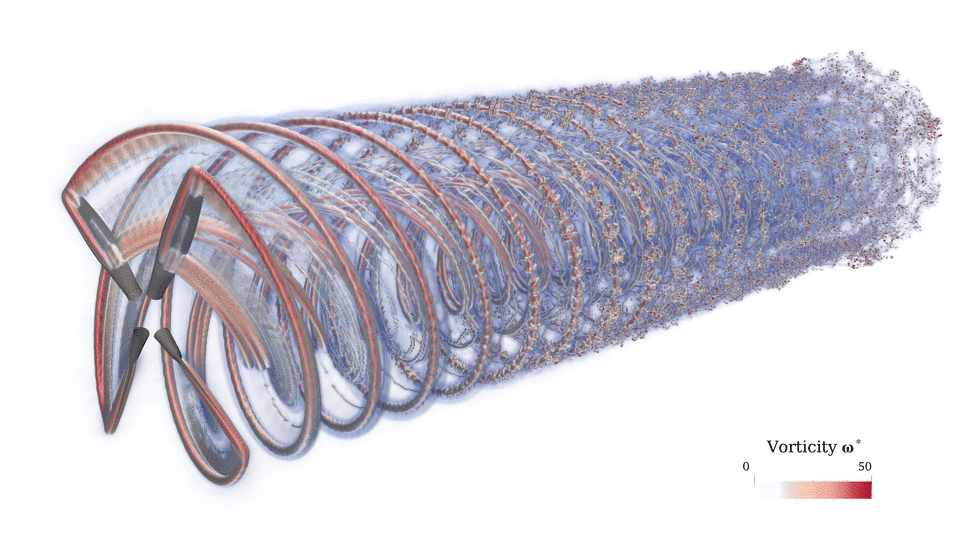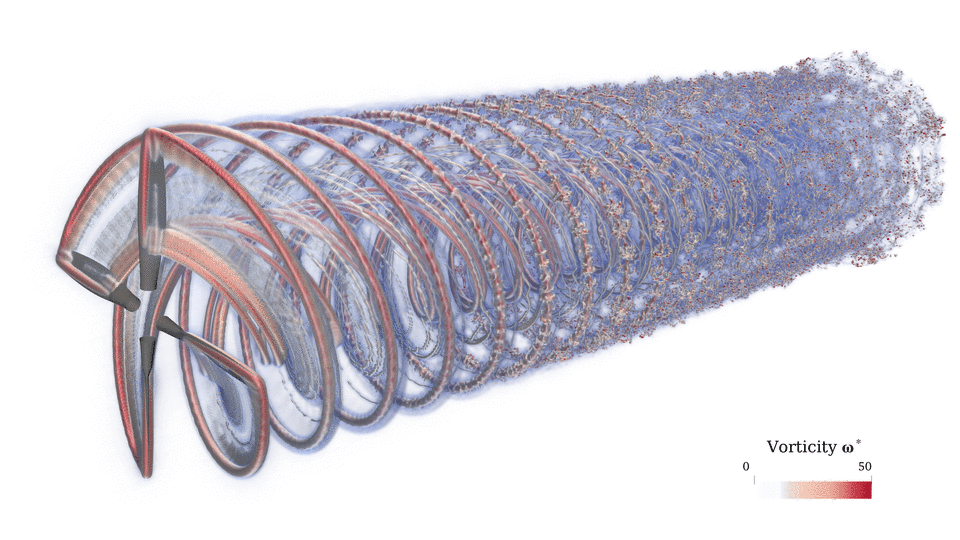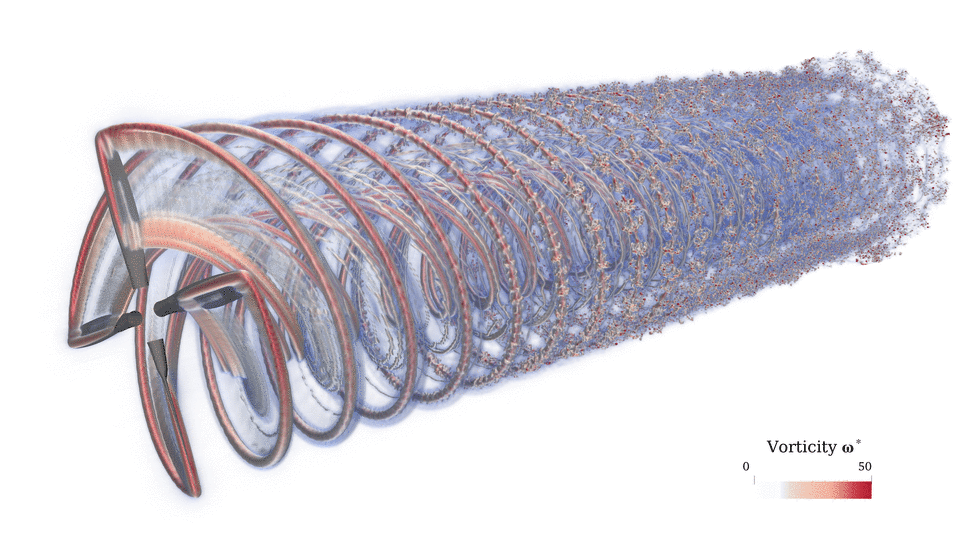
This meshless CFD has several advantages over conventional mesh-based CFD. In the absence of a mesh, the rVPM (1) does not suffer from the conventional CFL condition, (2) does not suffer from the numerical dissipation introduced by a mesh, and (3) derivatives are calculated analytically rather than approximated through a stencil. Furthermore, rVPM is highly efficient since it uses computational elements only where there is vorticity rather than meshing the entire space, making it 100x faster than conventional mesh-based LES.
FLOW VLM
Vortex lattice methodfor inviscid lifting surfaces
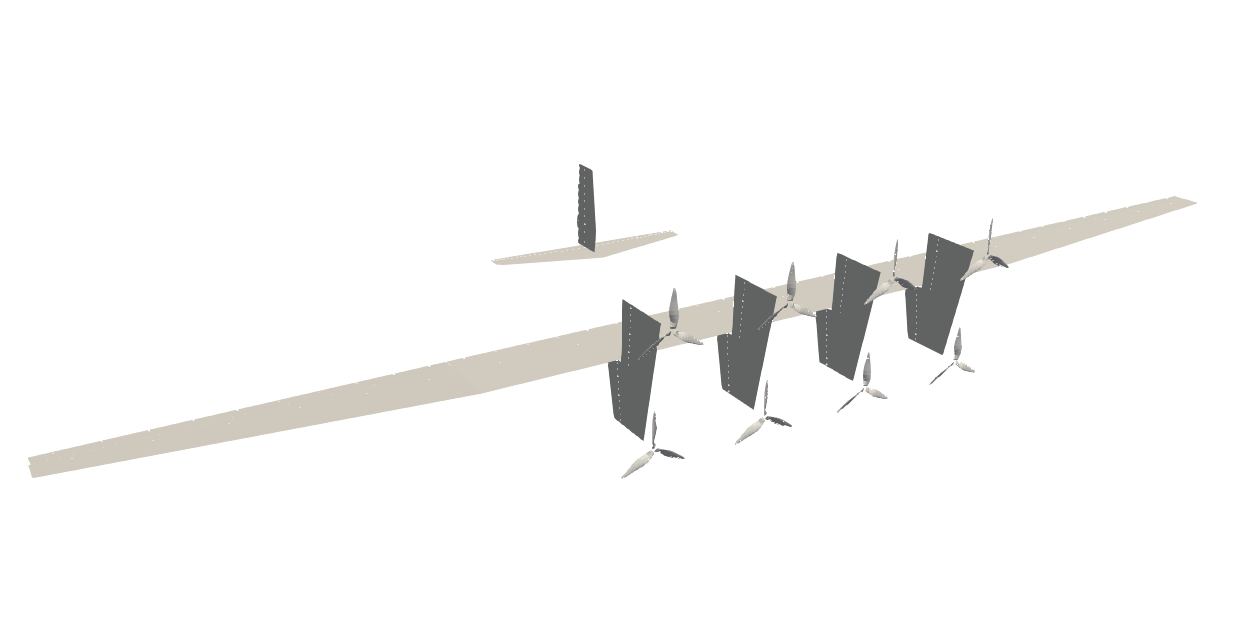
FLOWVLM is a VLM code implementing the discrete vortex Weissinger model (which uses only one chordwise horseshoe). It also implements a blade elements for the modeling of rotors (wake model is provided by the user), while also integrating with the BEMT code CCBlade.
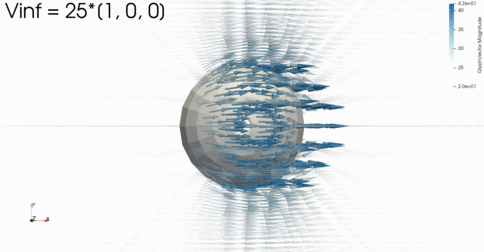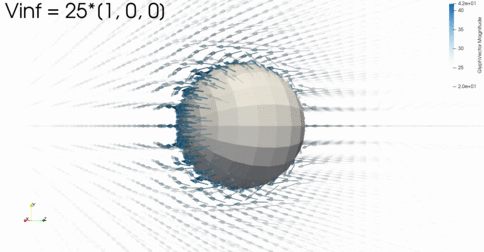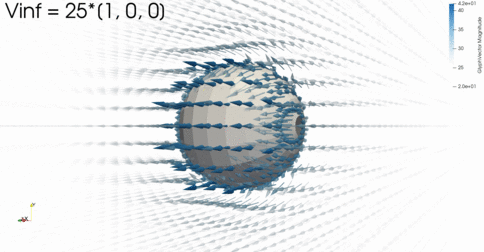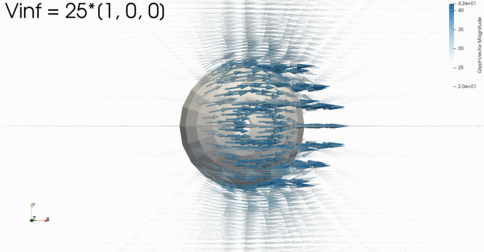
FLOW Panel
3D panel methodfor inviscid aerodynamics
FLOW Unsteady
Interactional aerodynamics and aerocoustics solverfor multirotor aircraft and wind energy
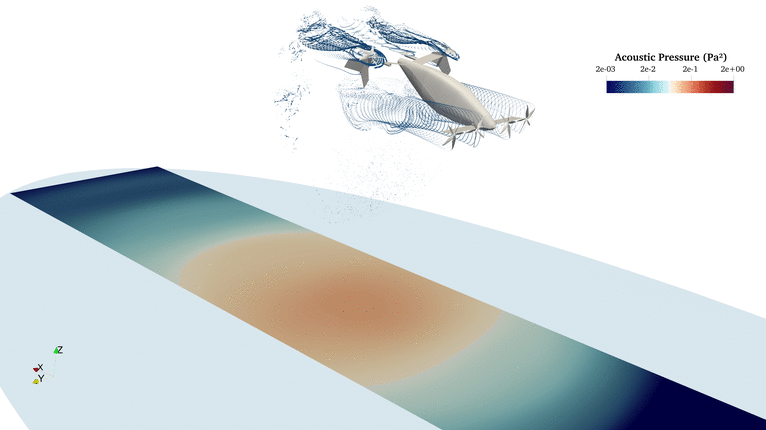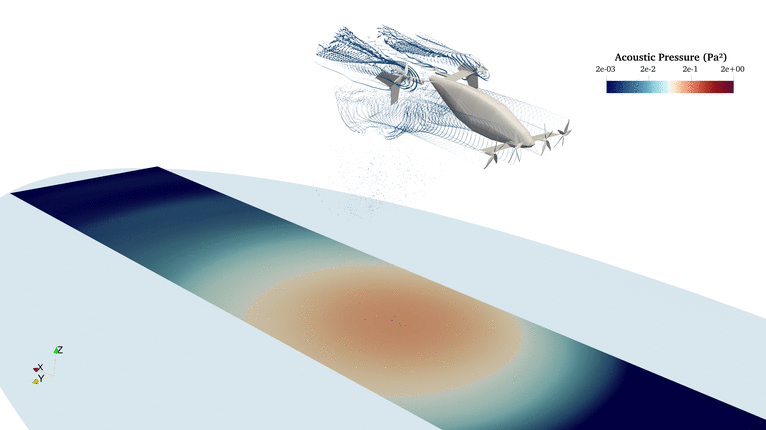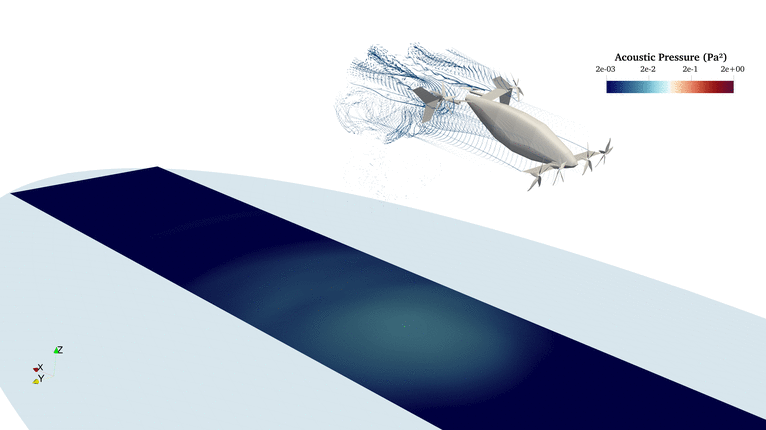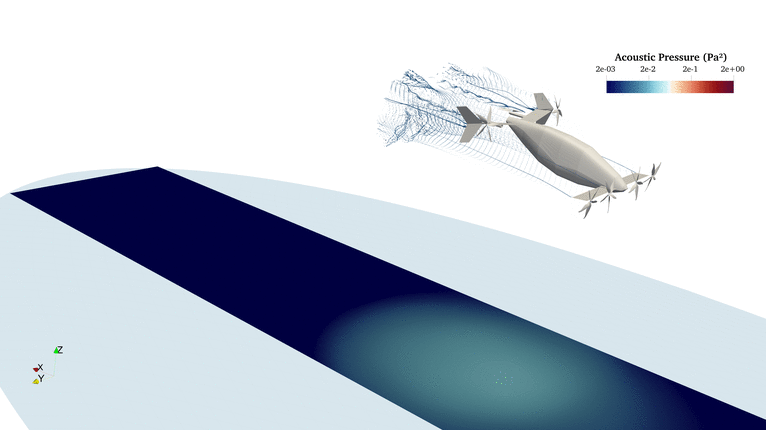
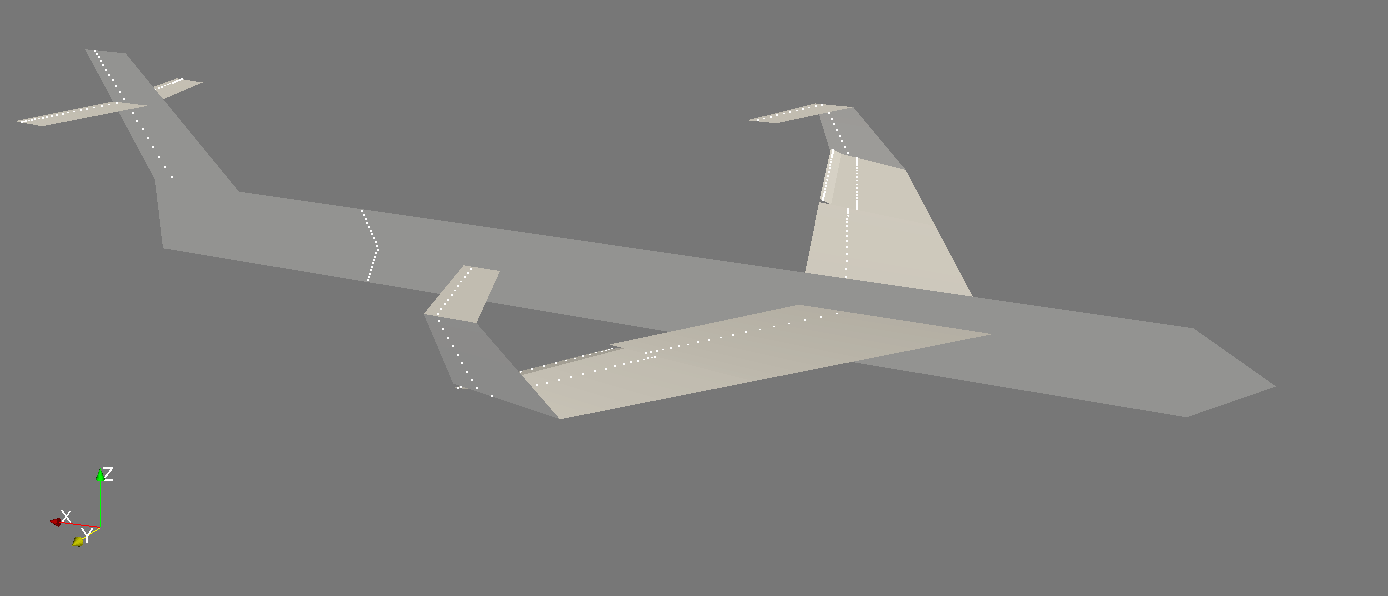
FLOWUnsteady is a variable-fidelity framework for unsteady aerodynamics and aeroacoustics based on the reformulated VPM. This suite brings together all the aerodynamics tools developed at BYU's FLOW Lab: Vortex lattice method, strip theory, blade-element momentum, 3D panel method, and the reformulated vortex particle method. The suite also integrates PSU-WOPWOP (FW-H solver) and a BPM code for tonal and broadband noise prediction.
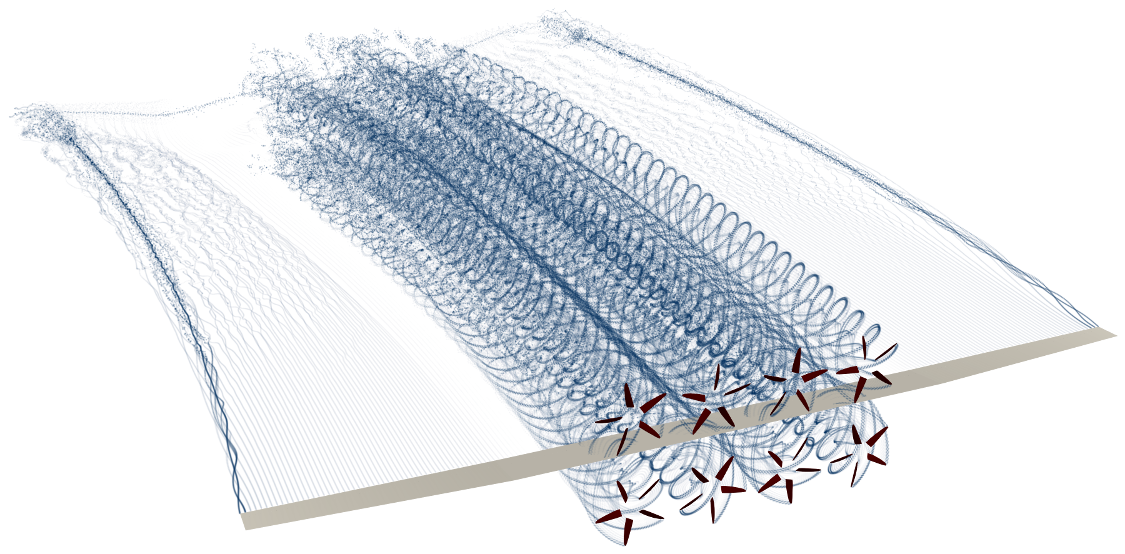
FLOWUnsteady solves all interactions (rotor-rotor, rotor-wing, and wing-wing effects) encountered by a vehicles along a prescribed maneuver, featuring rotors with variable RPM and tilting surfaces.